Residential & Commercial Fire Alarms: The Latest Innovations

Table of Contents
- 1 How Fire Alarm Technology Has Advanced
- 2 Types of Fire Alarm Systems for Diverse Needs
- 3 Benefits of Smart Integration with Building Automation
- 4 Key Fire Safety Codes and Standards Explained
- 5 Best Practices for Installation and Ongoing Maintenance
- 6 Understanding Costs and Long-Term Value
- 7 Trends Shaping the Future of Fire Alarm Systems
- 8 Frequently Asked Questions
How Fire Alarm Technology Has Advanced
Fire alarm systems have dramatically evolved from basic standalone smoke detectors to advanced, interconnected solutions. Today, systems deploy heat, flame, and even air quality sensors, and routinely communicate directly with residents or facility managers through smart devices. These developments have paved the way for faster emergency response and greater peace of mind—minimizing damage, saving lives, and ensuring business continuity. However, investing in such systems without fully understanding their capabilities, requirements, and legal obligations can lead to costly mistakes and missed safety opportunities.
The newest fire alarm panels harness digital intelligence and can self-diagnose technical issues, while some leverage machine learning algorithms to distinguish between real threats and nuisance alarms. According to NFPA Journal, these innovative features have sharply reduced false alarms and enhanced system responsiveness in residential and commercial environments.
Types of Fire Alarm Systems for Diverse Needs
Building type, occupancy, and functional goals all influence the choice of a fire alarm system. Addressable systems, ideal for properties like hotels, schools, and large offices, enable pinpoint detection and faster incident management. Conventional systems suit small to medium businesses or individual residential homes, offering reliability at a lower price point. On the other hand, aspirin smoke detectors are designed for precision and rapid reaction in mission-critical environments such as server rooms and hospitals.
As organizations and families prioritize flexible and scalable options, wireless and hybrid systems are gaining popularity. These systems allow for less invasive installation and easier future upgrades, especially when retrofitting older buildings.
Benefits of Smart Integration with Building Automation
Today’s modern buildings are becoming “smarter,” with fire alarm systems now seamlessly intertwined with wider building automation and security networks. For instance, when the alarm detects a threat, automated responses like unlocking exit doors, halting elevators, or shutting down HVAC systems can be enacted instantly. This supports fast, orderly evacuation and limits smoke and fire spread, safeguarding property and enhancing occupant safety.
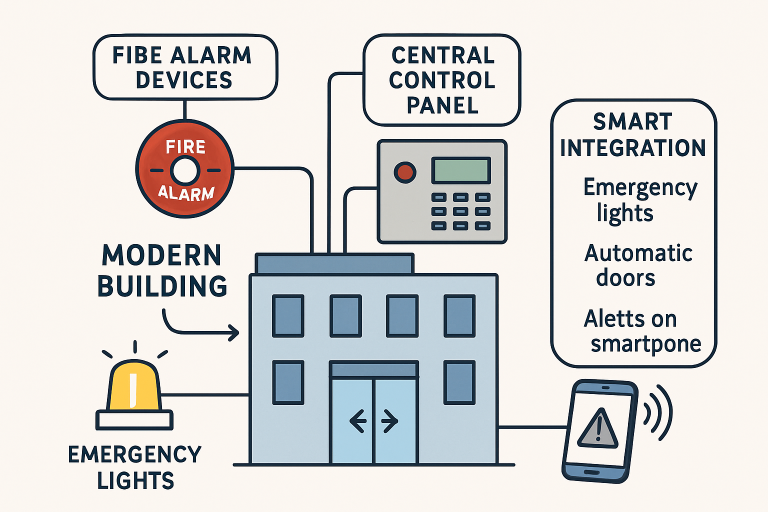
A study published by Security Info Watch highlights that integration with automation platforms is quickly becoming a standard in commercial developments, pointing to the value of better efficiency, lower operational costs, and easier code adherence.
Key Fire Safety Codes and Standards Explained
Adherence to established fire safety standards is non-negotiable for legal compliance and occupant protection. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) publishes comprehensive guidelines (like NFPA 72) that govern system design, installation, and maintenance. Local codes often layer additional requirements, emphasizing the importance of working with experts who understand evolving regulations in your region. Detailed attention to code doesn’t just shield against legal exposure—it plays a role in securing insurance coverage and meeting municipal approval.
For a deeper dive into code requirements and updates, the U.S. Fire Administration offers valuable public resources to help property owners and managers stay informed.
Best Practices for Installation and Ongoing Maintenance
- Always work with qualified, certified professionals who keep pace with the latest industry techniques and code changes.
- Conduct monthly user-level tests of alarms and detectors, ensuring all points are responsive and unobstructed.
- Arrange for annual inspections by authorized technicians, making repairs or component upgrades as needed.
- Train everyone on the premises, whether staff or family, on emergency procedures and how to interact with the alarm system.
Proactive upkeep isn’t only about ticking boxes for compliance but also about building a safety culture. Real-world incidents have shown that routine checks are critical—they catch problems such as misaligned sensors, expired batteries, or improper placements that can compromise detection and response.
Understanding Costs and Long-Term Value
While the initial installation of a modern fire alarm system may represent a significant investment, choices like wireless or fully integrated systems offer savings over time through reduced installation labor, ongoing flexibility, and minimizing future rewiring or technology obsolescence. The returns are measured in more than safety: many insurers provide discounts for robust, well-maintained fire alarm installations, and property values may rise.
Over the years, the reliability and adaptability of the chosen system have driven long-term value, reducing life-cycle costs and lessening the impact of fire-related incidents. For further guidance on insurance perspectives, the Insurance Information Institute covers relevant fire protection insurance topics in detail.
Trends Shaping the Future of Fire Alarm Systems
The future of fire alarm systems is converging with artificial intelligence, cloud connectivity, and automated diagnostics. AI-powered systems will enable earlier, more accurate alerts, and predictive maintenance will preemptively address faults before they become failures. These evolutions make alarms reactive and preventive tools within a larger innovative building ecosystem. Machine learning will enable better recognition of real threats versus non-emergency events, leading to fewer false alarms and less disruption for businesses and homeowners alike.
As smart city infrastructure and green building initiatives grow, expect fire alarm systems to take on broader roles in building health monitoring, energy management, and emergency communications, advancing safer, more connected environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How often should fire alarm systems be tested?
- Basic checks should occur monthly, with a comprehensive annual professional inspection to ensure code compliance and technical performance.
- Is smart integration worth it for smaller buildings?
- Absolutely. Even small—to medium-sized properties can benefit from integrated systems, which improve efficiency, facilitate system management, and speed up emergency response.
- What should building owners look for in a fire alarm provider?
- Certification, positive reviews, transparent service agreements, and a commitment to ongoing support are essential for ensuring a reliable solution.
Innovations in fire alarm technology are making homes and businesses safer, smarter, and more responsive. Property owners gain greater peace of mind with advancements in connectivity, detection accuracy, and integration with broader safety systems. Proactively adopting these solutions ensures stronger protection, faster response times, and improved overall resilience.






